Command-line Interface
Next to a graphical user interface, MonkeyCI also provides a command-line interface (or CLI). The CLI can be used to trigger builds, run them locally, verify build scripts or run unit tests.
Installation
In order to install the CLI, you will first need to install Java. You'll need Java 21 or later for the CLI to work correctly. Then run this script:
$ wget https://monkeyci-artifacts.s3.fr-par.scw.cloud/install-cli.sh -O - | bash
It will download the MonkeyCI jar file, put it in a local directory and create a binary that allows you to invoke it. The binary is installed in $HOME/bin, which usually is in your PATH. If it doesn't work, check if the bin dir has been added to your path.
Invocation
Running the CLI is done by invoking the monkeyci command:
$ monkeyci build --help
NAME:
build - Build commands
USAGE:
build [global-options] command [command options] [arguments...]
VERSION:
0.23.0
COMMANDS:
run Runs build locally
verify Verifies local build script
test Runs build script unit tests
GLOBAL OPTIONS:
-?, --help
Although there are other commands, they are intended for internal use and so only the build command will be discussed here.
Running Builds Locally
Runs a build locally. It will load the build script, and execute any jobs according to the configuration. For container jobs, podman is used. Note that local builds do not count towards your credit consumption, and it will also not register on the main application. Artifacts and caches are not downloaded or published.
This can be useful to run a one-of, or to try something out. For actual testing it's better to write unit tests. Below are the possible options you can pass to the command:
NAME:
build run - Runs build locally
USAGE:
build run [command options] [arguments...]
OPTIONS:
-d, --dir S .monkeyci Script location
-u, --git-url S Git repository url
-b, --branch S Repository branch
-t, --tag S Repository tag
--commit-id S Commit id
--sid S Repository sid
-p, --param S Build param
--params-file S Build params file
-?, --help
Normally, you will navigate to your git repository directory. There you will run the build command:
$ monkeyci build run
This will execute the build script found in the local .monkeyci/ directory. If you want to override this, you can use the -d switch. It's also possible to execute a build directory from a git repository, by passing in the --git-url. If you want to use a private repository, make sure your SSH-keys are configure correctly (in the ~/.ssh directory).
If you have an xterm-compatible terminal (like most are), you will also get a nice layout:
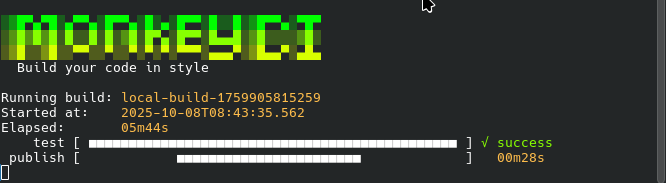
This gives you an overview of your build.
Parameters
By default, when running a local build, no parameters will be passed. In the future, we will add the possibility to fetch parameters from the global API, but this feature is still under development. You can, however, explicitly specify build parameters on the command line. Either by specifying them literally using the -p or --param option, or by putting them all in a file, and passing its path using the --params-file option. Each of these support multiple occurrances. For example:
$ monkeyci build test -p PARAM1=value1 -p PARAM2=VALUE2
Or, using a file:
$ monkeyci build test -p PARAM1=value1 --params-file params.edn
The --params-file option accepts edn, json, yaml or Java Properties files. A json parameters file could look like this:
{
"username": "testuser",
"password": "highly-secret-value"
}
These parameters are then passed to your build script, where they can be retrieved using the build-params api function.
(ns build
(:require [monkey.ci.api :as m]))
(m/action-job
"show-param"
(fn [ctx]
;; Will print the username value to the job output
(println "The username is:" (get (m/build-params ctx) "username"))))
Verifying Build Scripts
When you want to do a quick verification of your build script syntax, the build verify command is ideal. It does not run any jobs or tests, but it does a static code analysis of the build script itself, and will flag any syntax errors or warnings.
$ monkeyci build verify
Build script is valid!
It will either print out a success message, or list any errors and warnings it encounters.
Running Unit Tests
Runs any unit tests that you may have configured on your build script. See unit tests for more details.
Configuration
Not everything is configurable via command line arguments. Some more uncommon settings can be set via the configuration files. These are EDN files that are read at application startup. There is a global file located at /etc/monkeyci/config.edn and a user-specific file in $HOME/.config/monkeyci/config.edn. In addition, you can pass extra configuration files using the -c command line argument:
monkeyci -c /path/to/config.edn build run
You can specify multiple configuration files this way.
The files are read in this order:
- First the global file
- Then the user-specific file
- Then the files from the command line, in order.
This means that the global file has the lowest priority, settings can be overridden in the user file or those on the command line.
Configuration File Structure
The configuration file is hierarchical, so it's a tree of maps, where settings are grouped according to module.
Account Settings
The account information is used to access the MonkeyCI REST API when running builds locally. It resides under the :account key.
| Parameter | Meaning | Default |
|---|---|---|
:org-id | Id of the organization | |
:repo-id | Id of the repository | |
:url | URL of the MonkeyCI API | https://api.monkeyci.com/v1 |
:token | API key to access the API |
Example:
{:account
{:org-id "monkey-projects"
:token "my-very-secret-token"}}
Note that since the token is stored in plain text, we advise to either specify it on the command line, specify it as an environment variable (MONKEYCI_KEY), or ensure the configuration file can only be read by you.
Podman Settings
Podman is used to run local container. Its settings reside in the :podman key. These are the possible parameters:
| Parameter | Meaning | Default |
|---|---|---|
:podman-cmd | The path to the podman executable | /usr/bin/podman |
For example:
{:podman
{:podman-cmd "/usr/local/bin/podman"}}